Symptoms and causes of deep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition in which blood clots form deep inside the vein in the body. Blood clots may form when the blood flows slowly, resulting in clumping; this is known as clotting. DVT usually happens in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis. It can, in some cases, form in the other parts of the body too.
DVT can be fatal if the clot starts flowing through the arteries/veins of the lungs, causing pulmonary embolism. Knowing the causes and symptoms of DVT can help take quick action without having to face further consequences.
Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis
In most of the cases of DVT, there are no early signs. Only in later stages, the following symptoms can be seen:
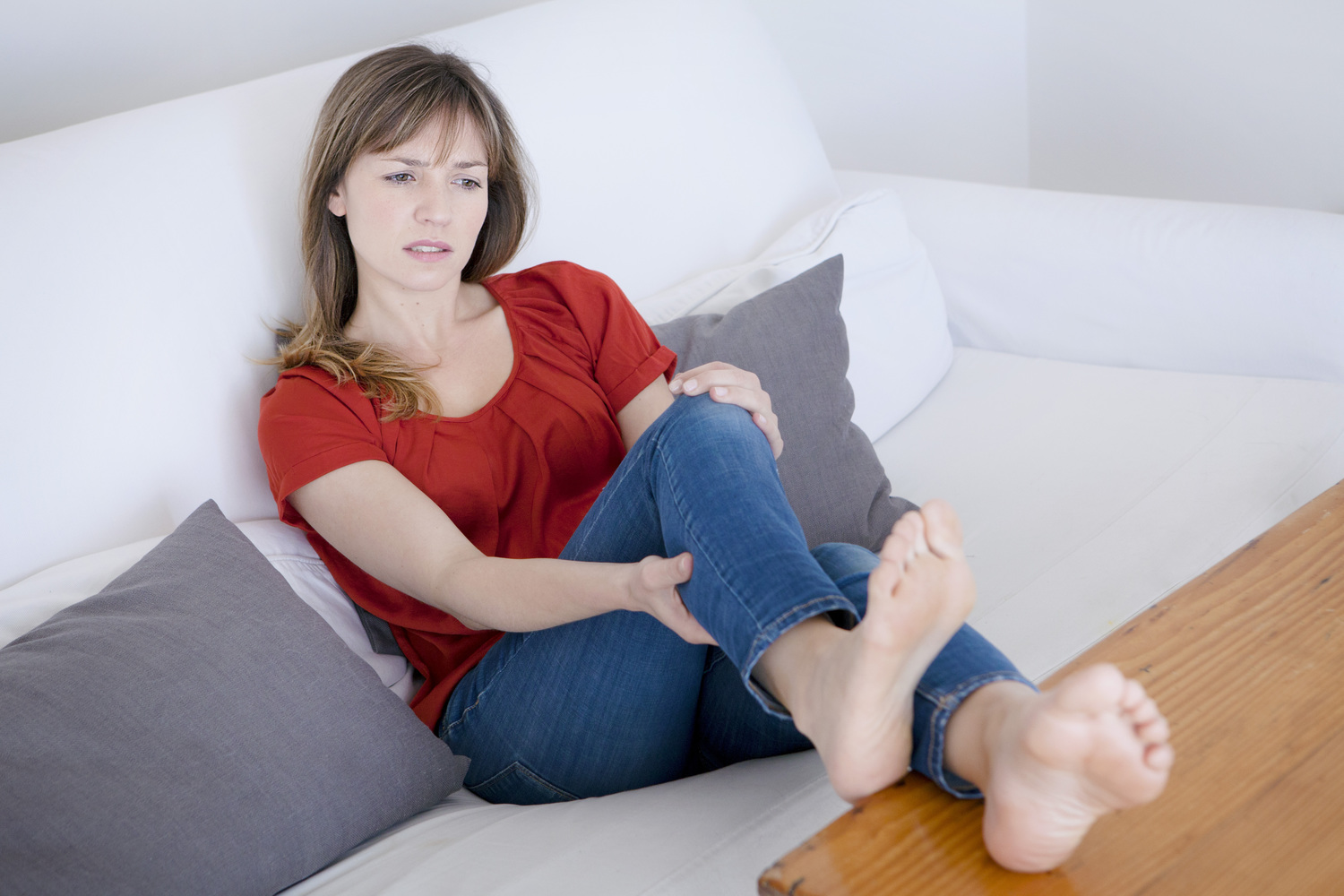
- Swelling in the leg or arm without any trigger.
- Soreness or pain when you walk or stand.
- Feeling warm in and around the affected areas.
- Redness of the skin. Sometimes it may also appear blue.
- Enlarged veins
Pulmonary embolism, which is a severe stage of DVT is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain that gets worse as you breathe in.
- High heart rate
- Coughing up blood
- Feeling lightheaded or dizzy
- Falling unconscious
Pulmonary embolism could be fatal and needs immediate medical attention.
Causes of deep vein thrombosis
- Sitting for longer periods
When you sit in one place for longer periods, the muscles in the legs stay relaxed. This slows the flow of blood to the legs, making it difficult to move around. This causes the clumping of the blood resulting in DVT. Frequent long car drives and long-haul flights can increase the risk. - Age
Although DVT can occur at any age, being 40 and above increases your risk of it. - Obesity
Body Mass Index (BMI) is the criterion that helps one determine if their height and weight in the ratio are normal or not. If your BMI does not match your current weight, you are most likely obese. This increases the chances of being affected by DVT. - Pregnancy
Pregnancy causes a woman’s body to go through various changes. Carrying a baby puts pressure on your legs and pelvis, which could sometimes cause DVT. In some cases, DVT occurs 6 weeks after childbirth. - Bed rest
Sometimes, after being advised for bed rest due to various health conditions, your muscles might remain still for a long time. This increases the risk of developing DVT as blood flow when lying down is usually slower. - Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or birth control pills
The estrogen in birth control pills or pills prescribed for HRT increase the chances of blood clot formation. This can also lead to DVT. In the case of the progesterone, when consumed as pills, there are no risks. - Smoking
Smoking has various health hazards. It tends to increase the viscosity of blood, thereby increasing the risk of DVT. It also affects the wall of blood vessels resulting in clotting.